PRESENT CRISIS IN IRAN
SARASIJ MAJUMDER
Iran officially is the Islamic Republic of Iran and is also known as Persia.
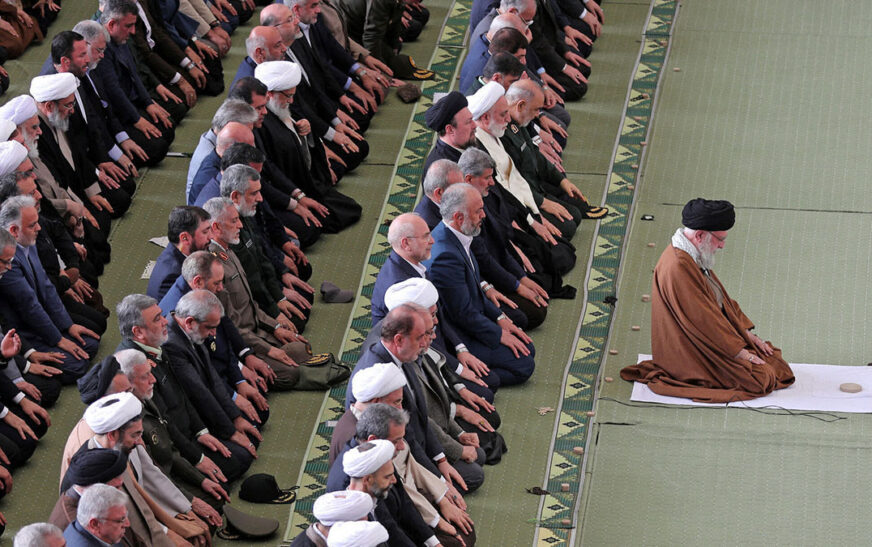
Supreme Leader is Ali Khamenei.
President: Masoud Pezeshkian # Capital: Tehran.
Iran is a predominantly Shia Muslim country, with Twelver Shi’ism as its official state religion. The vast majority of its Muslim population, estimated at 90–95%, is Shia.
Sunni Muslims are a significant minority in Iran, making up about 7.5% of the population.
Official State Religion: The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran mandates that the official religion of the state is Shia Islam and the Twelver Ja’fari school of jurisprudence.
Historical Shift: While Sunni Islam was the predominant form of Islam in Iran for centuries after the Arab conquest, this changed with the rise of the Safavid Empire in the early 16th century, which forcefully converted the population to Shia Islam to create a distinct national identity separate from the Sunni Ottoman Empire.
Sunni Population: Iran’s Sunni population is largely composed of ethnic minorities such as Kurds, Turkmen, Balochs, and Arabs, who primarily live in the northwest, northeast, and southeast border regions of the country.
Legal Status: Sunni Muslims are allowed to practice their faith and have representation in the Iranian parliament, but the law bars them from holding certain high-level government positions, such as the President or Supreme Leader.
WHAT CAUSED THE PRESENT CRISIS IN IRAN…?
Iran’s crisis is the result of: ECONOMIC SANCTIONS + POLITICAL REPRESSION + SOCIAL RESTRICTIONS + REGIONAL CONFLICTS+ ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS
- SEVERE ECONOMIC PROBLEMS : International sanctions (mainly by the US and its allies EU etc.) have reduced Iran’s oil exports, banking, and trade. The result is High Inflation, Unemployment, And Currency Devaluation. All these have reduced people’s purchasing power. Rising cost of food, fuel, and housing have caused public hardship. Due to the crisis, INFLATION hit the sky, 48.6% in October 2025 and 42.2% in December 2025
- US-IRAN TENSIONS & SANCTIONS: The crisis deepened after the deal (JCPOA). Nuclear Sanctions were reimposed to stop Iran’s nuclear and missile programs. These sanctions restrict foreign investment and isolated Iran from the global economy.
- POLITICAL UNREST & PROTESTS: Many Iranians protest against Economic Mismanagement, Corruptions, Restrictions on personal freedoms and for other social reformations.
- STRICT SOCIAL & RELIGIOUS CONTROLS: Iran follows a strict Islamic governance system. Laws on dress code, speech, media, and women’s rights have caused dissatisfactions, particularly among younger generations. Tensions between conservative leadership and a modern, educated population continue to grow. Limited freedom of expression, media, and political participation fueled the anger.
- REGIONAL CONFLICTS & FOREIGN POLICY COSTS : Iran supports groups in Lebanon (Hezbollah), Syria, Iraq, Yemen, and Gaza. These activities strain Iran’s economy and bring conflict with Israel, Saudi Arabia, and the US. Military. IRAN’s spending abroad is unpopular among citizens facing domestic hardship at home.
- NUCLEAR PROGRAM DISPUTE: Western countries fear Iran may develop nuclear weapons. Iran insists its program is for peaceful energy. This dispute keeps sanctions in place and raises the risk of military confrontation. Government of IRAN doesn’t come clean on this, so that sanction is withdrawn.
- ENVIRONMENTAL CRISIS: Iran faces water shortages, droughts, and pollution. Poor water management has harmed agriculture, reduced production of food and triggered peasants unrest.
FUTURE OF IRAN: IF THE PRESENT CRISIS PERSISTS and geopolitical challenges continue without meaningful reform or diplomatic breakthrough, the country is likely to face prolonged instability with serious domestic and regional consequences.
If Iran’s existing economics conditions are allowed to continue:
➤ Reduce oil revenues and foreign investment.
➤ Growth of informal economy and brain drain of skilled youth.
➤ Higher chances of military confrontation with Israel, and / or the US.
➤ Agricultural decline leading to rural distress and migration.
All above will lead to a bigger regional instability, and it was initiated by USA a few years ago, with the aim for a ‘REGIME’ change, and fomented.
INDIA & IRAN RELATIONS:
Both share ancient civilizational ties, strategic interests, and economic complementarities.
Historical Agreements: Foundation laid by the 1950 Friendship Treaty, further deepened by the 2001 Tehran and 2003 New Delhi Declarations.
(a) Iran has been a major supplier of crude oil to India.
(b) Chabahar port in Iran provides India access to Afghanistan and Central Asia. THIS IS A VITAL BYPASS TO PAKISTAN.
(c) Iran offers resources (oil, gas, fertilizers) while India provides engineering goods, pharma, and food, creating a natural basis for trade despite financial hurdles.
(d) Platforms like SCO and BRICS to foster common interests and promote a multipolar world order.
(e) Bilateral Mechanisms: Regular institutional dialogues (Joint Committee Meetings, Security Consultations) ensure ongoing discussion for further cooperation.
(f) India’s oil imports from Iran have fallen drastically due to sanctions, dropping from a significant share (around 13% in 2007-08) to negligible amounts, with reports in mid-2025 showing imports as low as 0.04% of India’s total needs, as India shifted heavily towards Russia, Iraq, and the UAE for its oil supply.
(g) Iran earned around $53 billion from oil exports in 2023 despite sanctions. I couldn’t collect the recent data.
A stable IRAN is good for INDIA in all respect.